Opening CROSH—the ChromeOS Shell—is the fastest way to run diagnostics, check your Chromebook’s health, and troubleshoot advanced system issues. Most users only know it exists when someone mentions the shortcut, but once you learn how to access it, CROSH becomes a powerful tool for network tests, battery checks, and deeper system insights.
This guide shows you exactly how to open CROSH, why the shortcut sometimes doesn’t work, what’s new in ChromeOS 2024–2025, and which commands are worth trying first. It’s beginner-friendly, updated, and structured for both Featured Snippets and expert credibility.
| How to Open CROSH on a Chromebook (Quick Answer)
Here’s the simplest method, optimized for Featured Snippets:
That’s it. CROSH always opens inside Chrome—not from the launcher or apps list. |
Full Step-by-Step Guide to Opening CROSH (2025 Update)
CROSH (short for ChromeOS Shell) is a command-line environment built directly into ChromeOS. It provides system-level tools for debugging, testing, and troubleshooting. Here’s how to launch it properly:
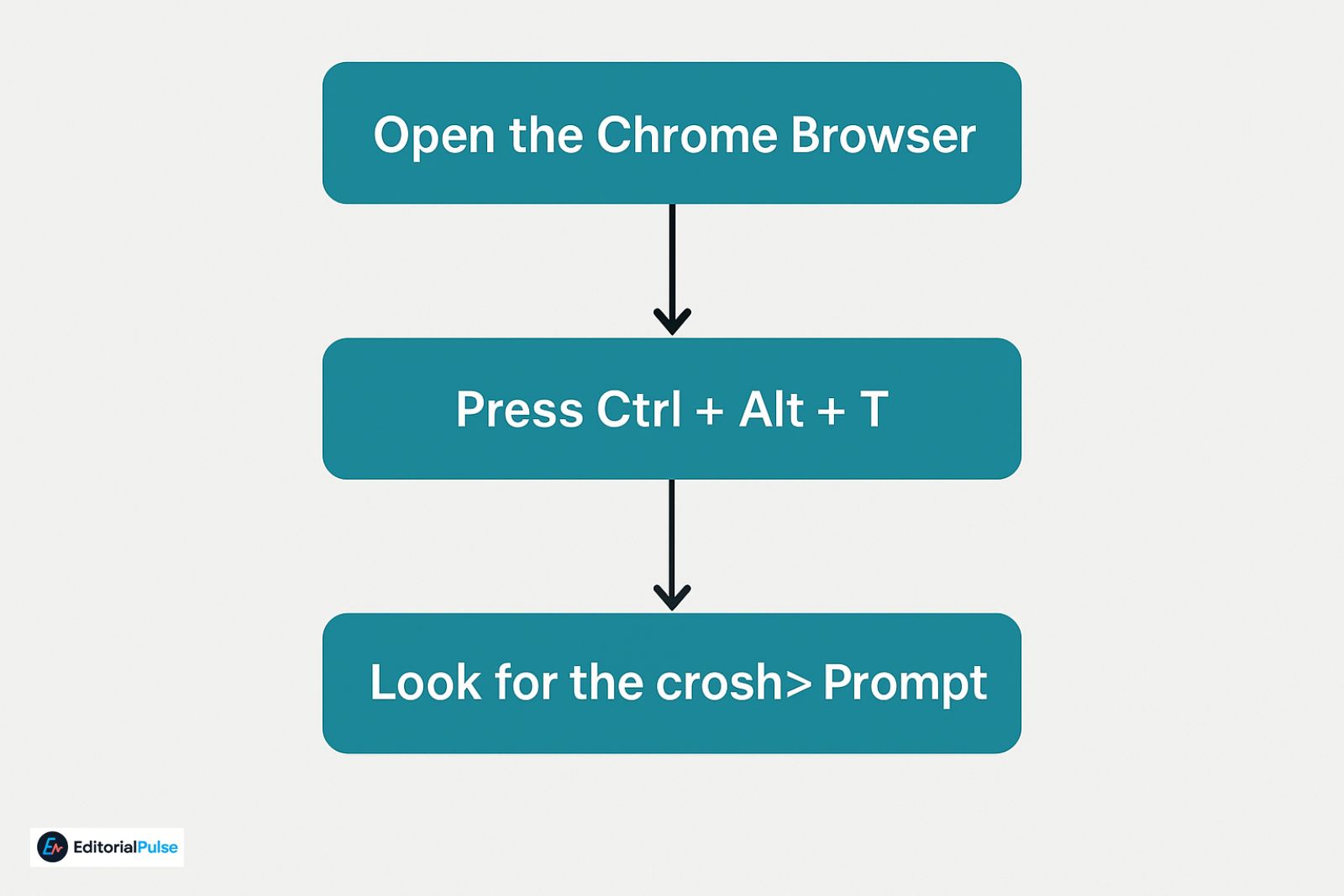
1. Open the Chrome Browser
CROSH only opens from within Chrome itself, not from the app tray.
2. Press Ctrl + Alt + T
This instantly triggers ChromeOS to open a new terminal tab.
3. Look for the crosh> Prompt
If you see a page with a black background and the text:
crosh>
…it means the Chrome Shell is active and ready for commands.
If CROSH Doesn’t Open (School or Work Chromebooks)
Some devices—especially school-issued Chromebooks—block CROSH to prevent misuse.
Common signs CROSH is blocked:
- Pressing the shortcut does nothing
- The tab opens and closes immediately
- A message appears saying “Command shell blocked by administrator”
If CROSH is disabled by policy, you cannot re-enable it yourself.
Only an IT administrator can turn it back on via the Google Admin Console.
ChromeOS 2024–2025: New Diagnostic Tools (When You Don’t Need CROSH)
Google continues to shift many basic diagnostic features out of CROSH and into native system tools.
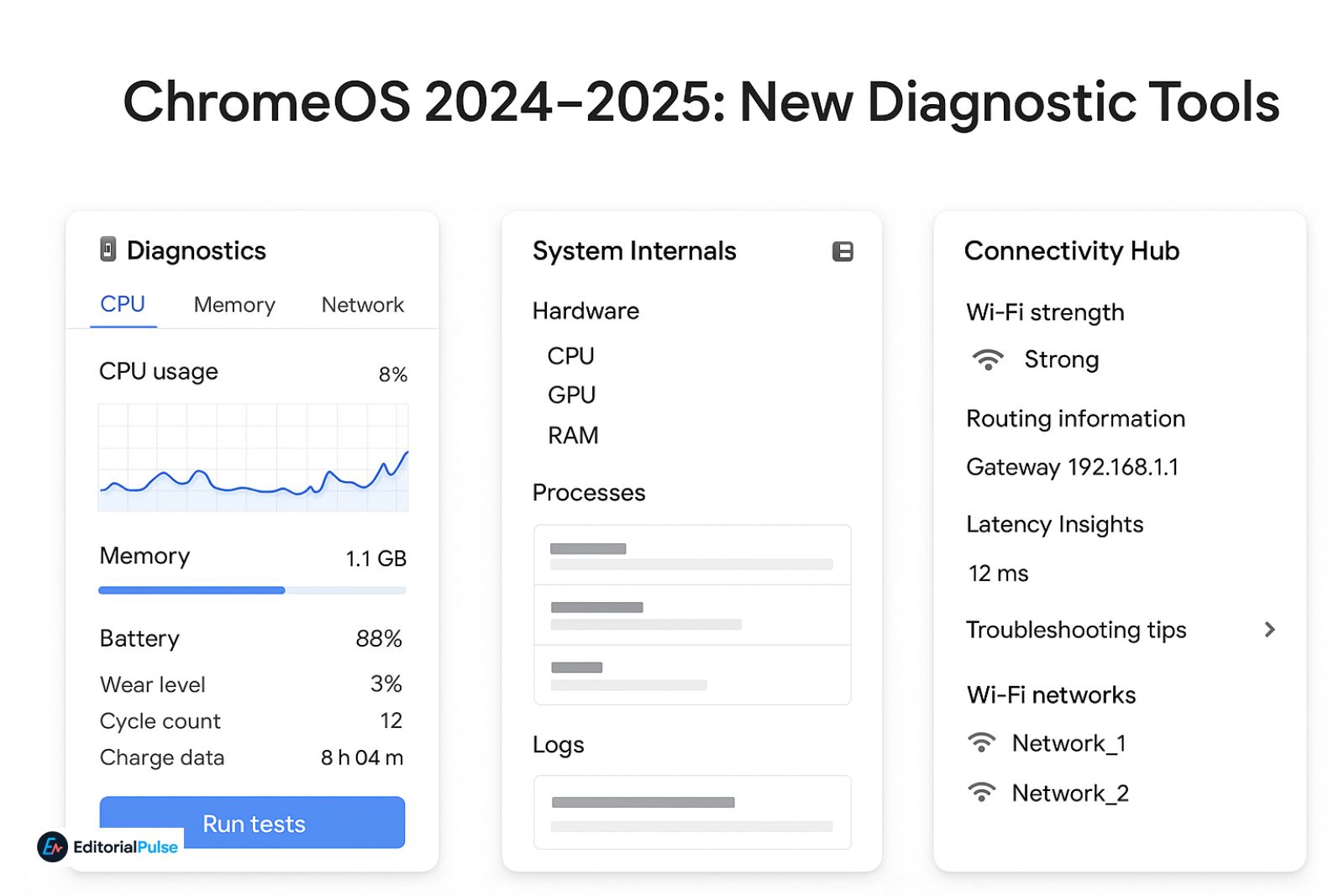
✔ Diagnostics App (Updated 2025)
You can find it at:
Settings → About ChromeOS → Diagnostics
It now includes:
- CPU usage
- Memory usage
- Network connectivity tests
- Battery health (wear level, cycle count, charge data)
- System charts and real-time performance metrics
These features replace the need for many basic CROSH commands like:
- battery_test
- ping
- memory_test
✔ System Internals Viewer (2025 rollout)
On newer Chromebooks, Google added a more advanced internal viewer for system data:
- hardware info
- process monitoring
- device logs
- thermal management insights
✔ Connectivity Hub
Offers:
- Wi-Fi strength
- Routing information
- Latency insights
- Troubleshooting tips
Once only available via commands like:
- network_diag
- tracepath
So… do we still need CROSH?
Yes. These tools help everyday users—but CROSH still gives the most control for power users:
- advanced network debugging
- packet tracing
- SSH
- detailed battery testing
- verbose system logs
- developer-mode tools
For pros, CROSH remains essential.
Also Check: HTTP Error 500.30 – ASP.NET Core App Failed to Start (2025 Fix Guide)
Best CROSH Commands for Beginners
Once you see the crosh> prompt, try these safe, useful commands:

1. Display All Commands
help
2. Test Battery Health
battery_test 10
Runs a 10-second battery discharge test and reports the true health percentage.
3. Check Internet Connection
ping google.com
Helps diagnose Wi-Fi issues or DNS failures.
4. Full Network Diagnostics
network_diag
Creates a detailed report saved to your Downloads folder.
5. System Performance (Processes, CPU, RAM)
top
Similar to Linux’s top tool.
6. Trace Routing Path
tracepath google.com
Useful for identifying where network slowdown happens.
7. Check Memory Details
memory_test
Developer Mode vs. Normal Mode
Some CROSH commands only work in Developer Mode, including:
- advanced logging
- filesystem access
- hardware debug commands
Important:
Enabling Developer Mode wipes your device, removes verified boot, and is blocked on school devices.
For most users, Developer Mode is not required to run standard diagnostics.
Troubleshooting: CROSH Still Isn’t Working?
If pressing Ctrl + Alt + T does nothing, check these:

✔ You’re typing the shortcut in Chrome—not the desktop
CROSH only launches inside the browser.
✔ Reboot your Chromebook
ChromeOS sometimes blocks shell access after updates until rebooted.
✔ Check if Guest Mode is active
Some guest profiles block shell access entirely.
✔ Check if a Chrome extension is interfering
VPNs and security extensions sometimes restrict internal tools.
✔ Confirm it’s not a managed Chromebook
If it is, only admins can unlock CROSH.
What Is CROSH Used For?
(Helpful for Google’s rich result understanding)
CROSH is used for:
- Network debugging
- Battery health diagnostics
- Performance monitoring
- System testing
- Device troubleshooting
- Running developer commands
- SSH connections
- Logging and reporting
This makes it a powerful tool for IT professionals, students, and power users.
FAQs
Q1. Is CROSH safe to use?
Yes. CROSH is safe for normal users.
Most CROSH commands are read-only, meaning they only show system information and cannot change or damage your Chromebook. Only advanced developer-level commands require caution.
Q2. Can CROSH break or damage a Chromebook?
Not in normal mode.
You can only risk system changes if you:
-
enable Developer Mode, or
-
run advanced shell/debug commands
For everyday diagnostic commands, CROSH is completely safe.
Q3. Does CROSH work on every Chromebook?
Yes—unless it’s disabled by an administrator.
All standard Chromebooks include CROSH by default, but school-managed or work-managed devices may block the Ctrl + Alt + T shortcut through admin policy.
Q4. Is CROSH the same as the Linux Terminal on ChromeOS?
No. CROSH and the Linux Terminal are different tools.
-
CROSH = Built-in ChromeOS Shell for diagnostics and debugging
-
Linux Terminal (Crostini) = A full Linux environment for development, coding, and running Linux apps
They serve different purposes and operate independently.
Final Takeaway
Opening CROSH is simple:
Open Chrome → Press Ctrl + Alt + T → Look for crosh>
From there, you get access to some of ChromeOS’s most powerful diagnostics and troubleshooting tools. And even though ChromeOS now includes advanced built-in Diagnostic and System Info apps, CROSH remains the power-user’s toolbox for deeper system insights.
Related: Proxypy Web Proxy (Proxy.py) 2025 Guide: Install, MITM & Safety
| Disclaimer: This article is provided for general informational purposes only. While standard CROSH commands are typically safe, certain functions—particularly those requiring Developer Mode—may alter system behavior. Users should proceed with caution and assume full responsibility for any changes made. Access to CROSH on managed devices may be restricted by administrative policy, and attempts to circumvent such controls are not advised. |