
Why Critical Thinking Matters More Than Ever
Artificial intelligence can now write essays, solve complex problems, summarize research papers, and generate confident answers in seconds. Tools like ChatGPT, Copilot, and Gemini are becoming everyday companions for students, professionals, and decision-makers. This rapid adoption raises a critical question: what happens to human critical thinking skills in the age of AI?
Search trends around critical thinking skills in the age of AI and AI vs critical thinking reveal growing concern. Many people worry that constant AI assistance may reduce independent thinking, weaken problem-solving abilities, or create overreliance on machine-generated answers. At the same time, others argue that AI can enhance learning and reasoning when used correctly.
This article takes a clear, evidence-based approach. It explains how AI actually affects critical thinking, what research suggests, and how individuals, students, educators, and professionals can use AI without losing the ability to think critically. The goal is not to reject AI—but to understand how to work with it intelligently.
What Are Critical Thinking Skills in the Age of AI?

Critical thinking skills in the age of AI refer to the human ability to analyze, question, and evaluate information generated or assisted by artificial intelligence, rather than accepting AI outputs at face value. These skills include assessing evidence, identifying assumptions, detecting bias, and making context-aware judgments that AI systems cannot reliably perform.
In simple terms, critical thinking ensures AI is used as a support tool, not a substitute for human reasoning.
AI vs Critical Thinking
| Aspect | Artificial Intelligence | Critical Thinking |
|---|---|---|
| Generates answers | Yes | Yes |
| Understands meaning | No | Yes |
| Questions assumptions | No | Yes |
| Evaluates truth | Probabilistic | Contextual |
| Takes responsibility | No | Yes |
Key insight: AI produces outputs. Critical thinking determines whether those outputs are accurate, ethical, and useful.
What Is Critical Thinking? (Quick Clarification)
Critical thinking is not the same as intelligence or knowledge. It is a skill set that includes:
-
Analyzing information objectively
-
Evaluating evidence and sources
-
Recognizing bias and logical fallacies
-
Drawing reasoned conclusions
-
Reflecting on one’s own thinking (metacognition)
These skills are essential in environments where information is abundant—and increasingly generated by machines.
How AI Changes Critical Thinking Skills (What’s Really Happening)
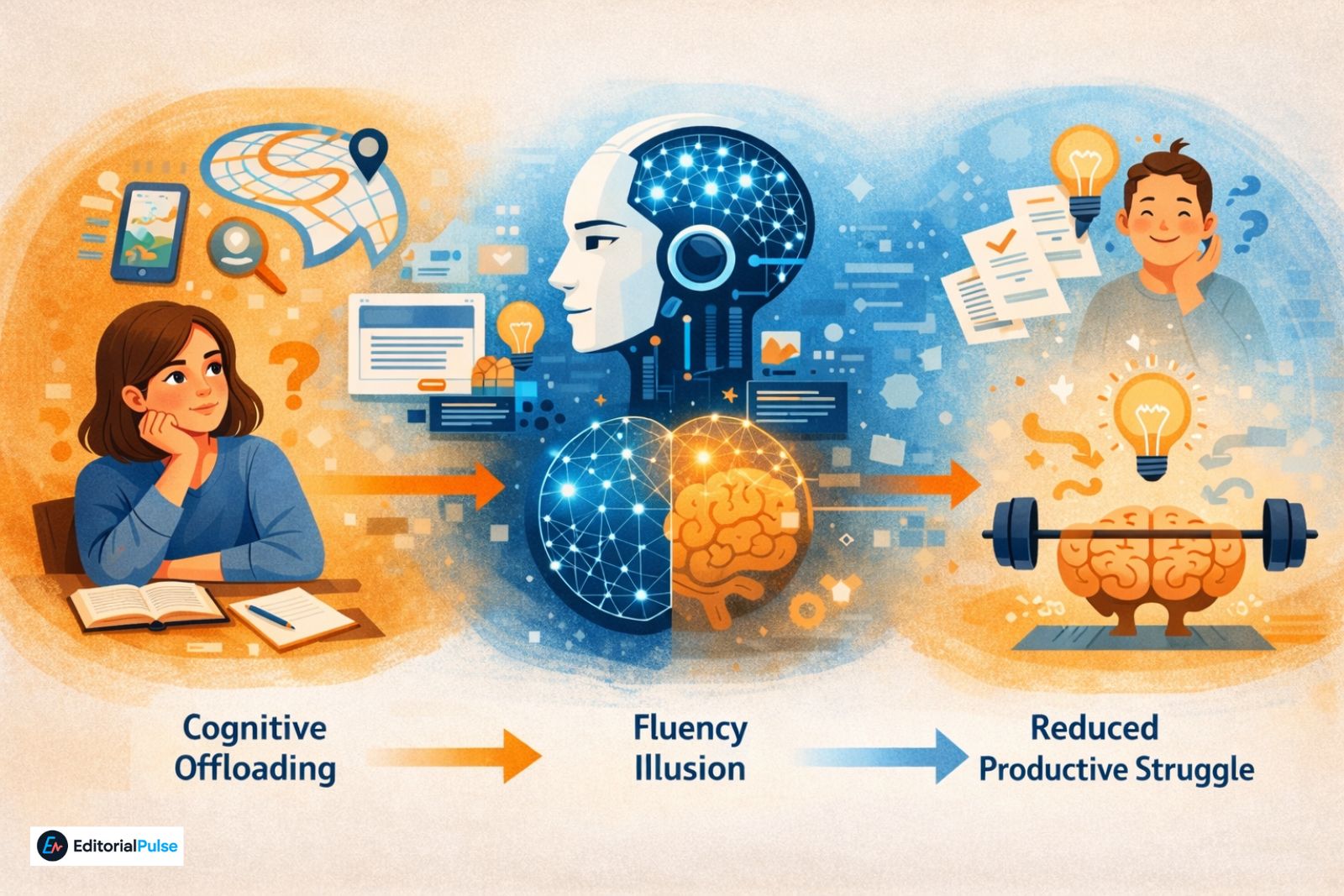
1. Cognitive Offloading
One of the most important mechanisms behind AI’s impact on thinking is cognitive offloading—the act of shifting mental effort to external tools.
Examples include:
-
Using calculators instead of mental math
-
Relying on GPS instead of spatial reasoning
-
Using AI to generate explanations instead of reasoning through them
Cognitive offloading is not inherently harmful. However, when AI replaces thinking rather than supporting it, critical thinking skills can weaken through lack of use.
2. The Fluency Illusion
Generative AI produces responses that are:
-
Well-written
-
Logically structured
-
Confident in tone
This creates a fluency illusion, where users assume that clear language equals correct reasoning. In reality, AI can present inaccurate or biased information very convincingly. Without critical evaluation, users may accept incorrect outputs as truth.
3. Reduced Productive Struggle
Deep learning often requires effort, confusion, and revision. AI reduces friction by offering instant answers. While this improves efficiency, it can also reduce opportunities for productive struggle, which is essential for developing strong reasoning skills—especially in students.
ChatGPT and Critical Thinking: What Research Suggests
Current research does not show that ChatGPT or similar tools automatically erode critical thinking. Instead, outcomes depend on how AI is used.
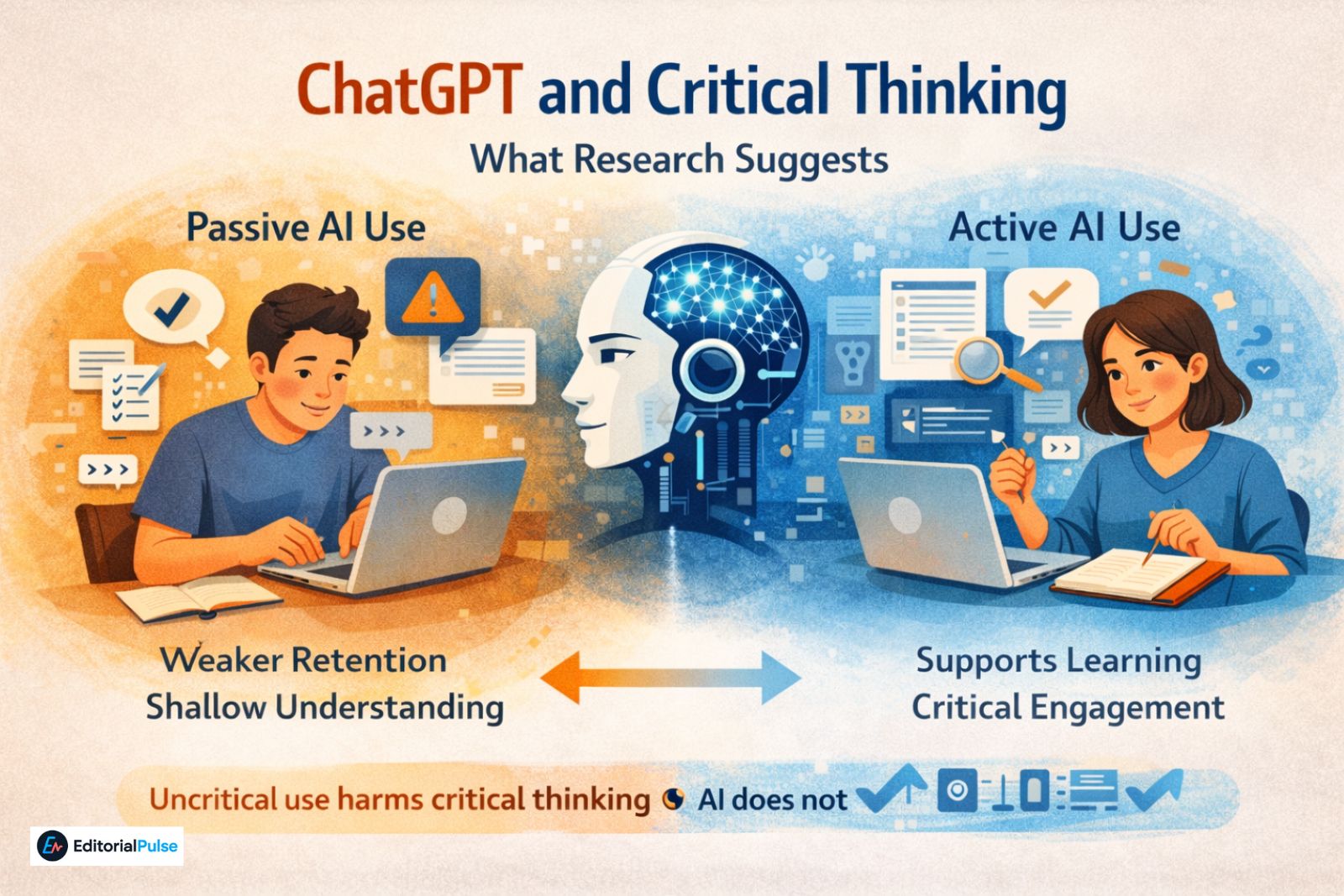
Across multiple educational and cognitive studies, patterns consistently emerge:
-
Passive AI use correlates with weaker retention and shallow understanding
-
Active AI use—questioning, revising, and critiquing outputs—supports learning
-
Verification tasks increase critical engagement
-
Over-trust in AI leads to error propagation
The conclusion is clear: AI does not harm critical thinking; uncritical use does.
AI and Critical Thinking in Education

Effects of AI on Students’ Critical Thinking
Students increasingly use AI for:
-
Essay drafts
-
Homework solutions
-
Research summaries
The primary risk is not plagiarism alone. The deeper issue is that students may skip key cognitive stages such as:
-
Problem framing
-
Hypothesis generation
-
Argument construction
When these stages are bypassed, students may produce correct-looking work without developing reasoning skills.
What Actually Works in Educational Settings
Educators who report positive outcomes with AI tend to:
-
Require students to critique AI-generated responses
-
Ask learners to explain reasoning in their own words
-
Introduce AI after initial independent thinking
-
Assess thinking processes, not just final answers
This approach positions AI as a thinking aid, not a thinking replacement, reinforcing the same human-first principle highlighted in discussions around unblocked browsers.
A Practical Framework: The C.A.R.E. Method
To preserve critical thinking skills in the age of AI, use the C.A.R.E. framework:
C — Conceptualize First
Define the problem and outline your approach before using AI.
A — Analyze the Output
Check logic, assumptions, and missing context.
R — Reason Independently
Ask whether your conclusion would change without AI input.
E — Explain Without AI
If you cannot explain the reasoning yourself, understanding is incomplete.
This framework helps prevent overreliance while still benefiting from AI efficiency.
Common Mistakes That Weaken Critical Thinking
-
Using AI before attempting to think independently
-
Accepting AI summaries instead of reading original sources
-
Confusing speed with understanding
-
Letting AI frame the problem instead of questioning it
-
Failing to audit AI confidence against evidence
These habits, if repeated, can gradually reduce analytical depth.
Critical Thinking in the Workplace: Why It Still Matters
In professional environments, AI increasingly supports:
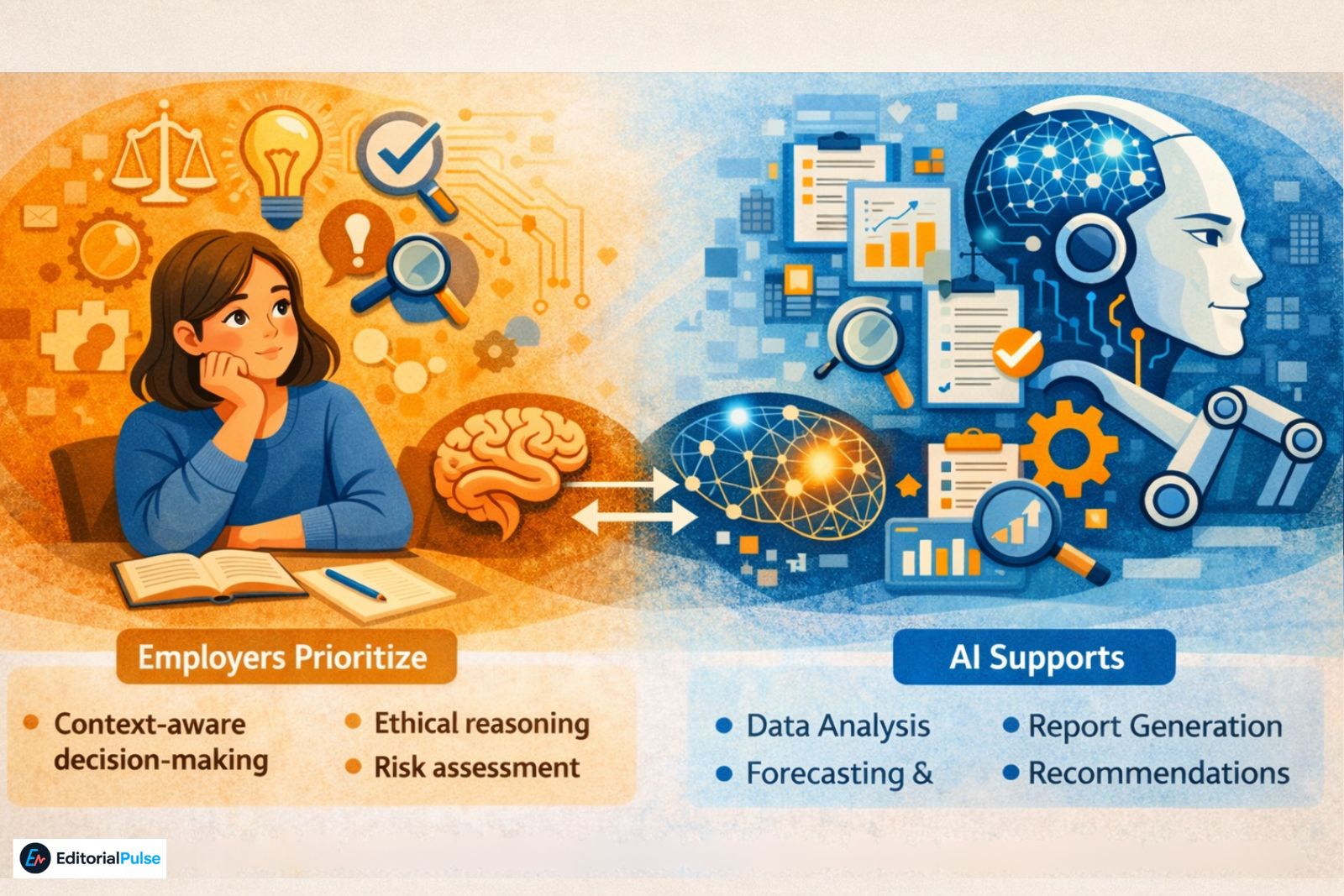
-
Data analysis
-
Report generation
-
Forecasting and recommendations
As execution becomes automated, judgment becomes more valuable. Employers continue to prioritize:
-
Context-aware decision-making
-
Ethical reasoning
-
Risk assessment
-
The ability to challenge flawed recommendations
In the age of AI, critical thinking is not obsolete—it is a competitive advantage.
The Future of Critical Thinking in the Age of Generative AI
Trends to Watch (2025 and Beyond)
-
AI-assisted assessments focused on reasoning, not recall
-
Hiring processes that test explanation and judgment
-
Increased emphasis on AI literacy combined with critical reasoning
-
Reduced value of rote memorization
Contrarian but evidence-aligned insight:
As AI raises the baseline of productivity, critical thinking determines who excels.
Practical Checklist: Using AI Without Losing Critical Thinking
Before accepting any AI-generated output, ask:
-
What assumptions does this rely on?
-
What evidence is missing or unclear?
-
What would happen if this were wrong?
-
Can I defend this conclusion without AI?
If the answer is no, more thinking is required.
FAQs
Q1. Why is critical thinking important when using artificial intelligence?
Critical thinking is important when using artificial intelligence because AI systems generate responses based on probability, not understanding or truth. Human judgment is needed to verify accuracy, assess context, and identify bias, especially in education, healthcare, and decision-making.
Q2. Does AI reduce critical thinking skills?
AI does not inherently reduce critical thinking skills. However, passive reliance on AI—without questioning or verification—can weaken reasoning over time. Active use that involves evaluation and reflection can support critical thinking development.
Q3. What is the difference between AI and critical thinking?
AI generates information using patterns from data, while critical thinking involves conscious reasoning, evaluation, and judgment. AI produces outputs, but critical thinking determines whether those outputs are reliable or appropriate.
Q4. How can students use AI without harming critical thinking?
Students can protect critical thinking by attempting tasks independently first, using AI for feedback rather than answers, verifying sources, and explaining conclusions in their own words.
Q5. Is critical thinking still relevant in the age of generative AI?
Yes. Critical thinking is more relevant than ever because AI-generated content must be evaluated for accuracy, bias, and ethical implications. As AI becomes more powerful, human judgment becomes increasingly valuable.
Conclusion: Reframing AI vs Critical Thinking
The real issue is not whether AI replaces critical thinking. It is whether people choose convenience over cognition.
Critical thinking skills in the age of AI are not disappearing—they are being tested. Those who actively evaluate, question, and reason will benefit most from AI’s capabilities. Those who rely on it blindly risk losing depth and independence.
AI can generate answers.
Only humans can decide which answers deserve trust.
Related: Digital Detox: A Practical 2025 Guide to Reclaiming Focus and Control
| Disclaimer: This content is provided solely for educational and informational purposes and is based on general research findings and insights available as of 2025. It does not constitute professional, academic, legal, or medical advice. Readers are encouraged to independently verify information and exercise their own judgment when interpreting or applying the material presented. |



