Google quietly records a significant amount of activity in the background. Every search, many app interactions, and even some voice commands can be tied to a single Google account setting: Web and App Activity.
Most users only notice it after seeing highly personalized search results, targeted ads, or a growing activity log inside My Activity. That’s when the real questions start: What exactly is being tracked? Where is it stored? And should this be turned off?
This guide explains what Web and App Activity actually is, how it works on desktop, Android, and iPhone, how to view or delete your activity, and how to decide—practically—whether leaving it on makes sense in 2025. Instead of generic instructions, you’ll get clear trade-offs, real-world behavior, and privacy-first configuration guidance.
What Is Web and App Activity?
Web and App Activity is a Google account setting that saves your interactions with Google services while you’re signed in.
It can include:
-
Google searches
-
Websites visited through Chrome when you’re signed into your Google account, Chrome sync is enabled, and Web & App Activity is turned on
-
Activity from Google apps such as Maps, YouTube, and Play Store
-
App usage data on Android devices
-
Voice and audio interactions with Google Assistant
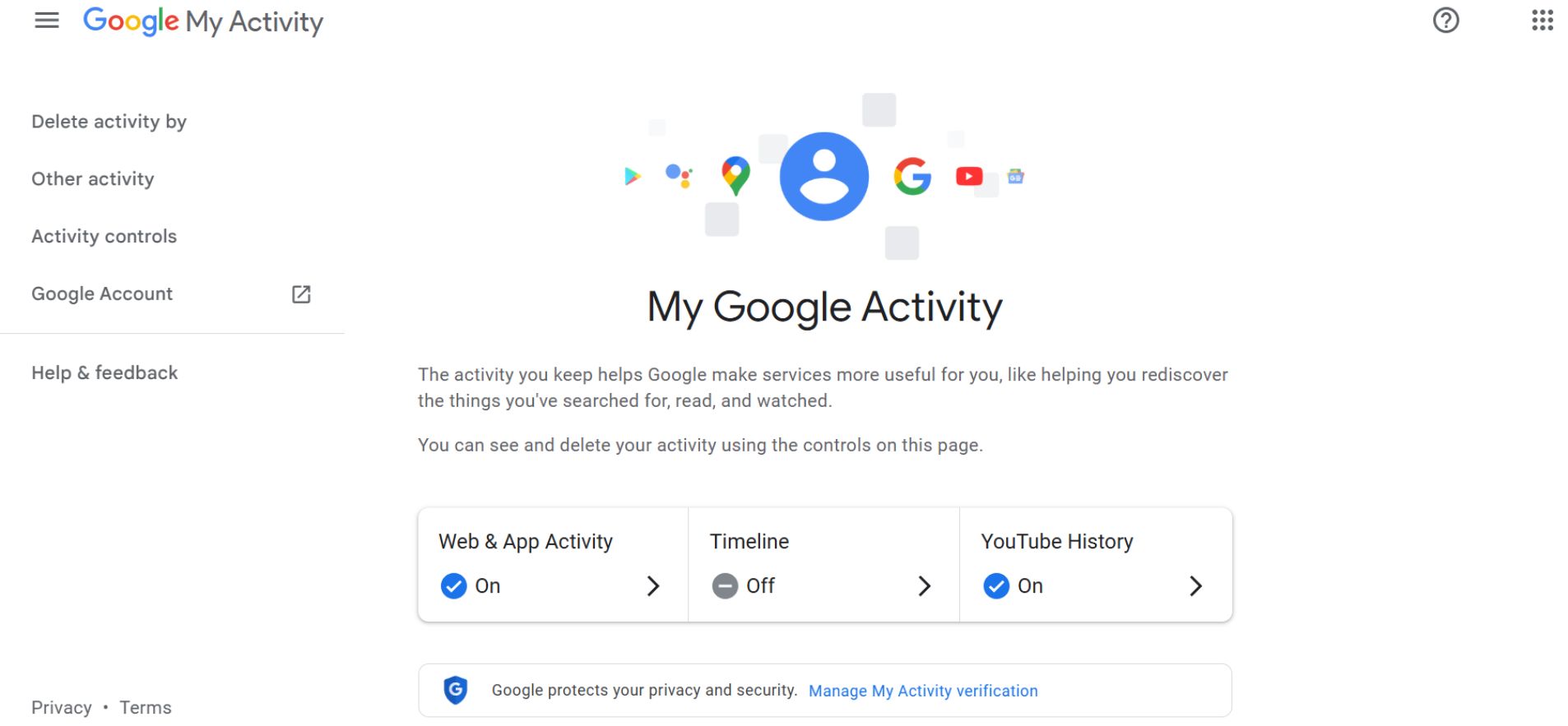
All of this data is stored under your Google account and shown in Google My Activity.
According to Google’s activity controls documentation, this information is used to improve search accuracy, personalize services, and provide faster, more relevant results across Google products.
Where Is Web and App Activity Stored?
Web and App Activity is stored in a centralized dashboard called Google My Activity.
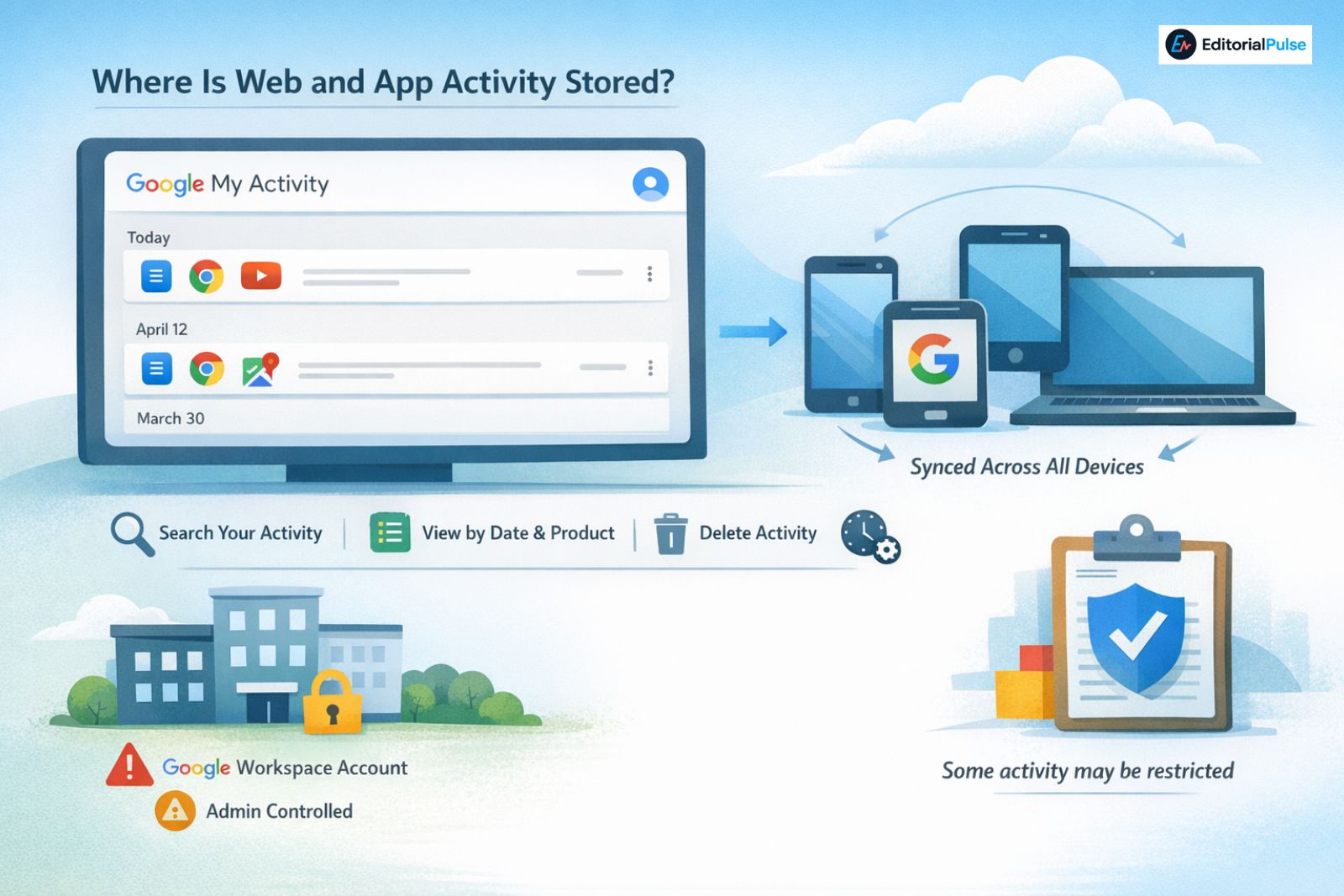
From there, you can:
-
View activity by date or Google product
-
Search past actions
-
Delete individual items or full time ranges
-
Manage activity controls and auto-delete rules
This data is account-based, not device-specific. If you’re signed into the same Google account on multiple devices, activity from all of them can appear in a single timeline.
Note: If you use a Google Workspace account (for work or school), some Web and App Activity settings may be managed by your administrator. In those cases, certain activity may not be visible to you or fully deletable on a company- or school-managed device
Web and App Activity on Desktop (Windows, macOS, Linux)
On desktop computers, Web and App Activity tracks behavior related to your browser and Google services, not your entire operating system.

What Gets Recorded on Desktop
-
Google searches while signed in
-
Websites visited in Chrome only when you’re logged into Google, Chrome sync is enabled, and Web & App Activity is turned on
-
Activity within Google services such as Gmail, Maps, Drive, and YouTube
What Is Not Recorded
-
Activity in non-Google desktop applications
-
Browsing in other browsers (unless you’re signed into Google there)
-
Local files or operating-system-level actions
You can manage desktop activity through Google My Activity or Google Account → Data & Privacy → Activity Controls. Any changes apply across all devices linked to your account.
Web and App Activity on Your Phone (Android & iPhone)

On Android
Web and App Activity is more deeply integrated and may include:
-
Google searches
-
Interactions within Google-owned apps and services
-
Voice commands and Assistant interactions
-
App usage tied to your Google account
You can manage this through Settings → Google → Manage your Google Account → Data & Privacy.
On iPhone
On iPhone, Web and App Activity still applies when you use:
-
Google Search
-
Google Maps
-
YouTube
-
Chrome (while signed in)
Apple’s Safari history remains separate, but activity within Google apps is still saved under your Google account.
Also Check: Anti Detect Mobile Browser (2025): Android vs iOS, Real Solutions Explained
How Web and App Activity Affects Your Google Experience
When It’s On
-
More relevant search results
-
Faster autocomplete suggestions
-
Better Google Assistant accuracy
-
Smarter Maps and Discover recommendations
-
More personalized ads
When It’s Off
-
Search results become more generic
-
Assistant loses contextual awareness
-
Recommendations reset
-
Ads continue, but with reduced relevance
This trade-off explains why many users feel Google “works worse” after disabling the setting.
Web and App Activity vs Other Tracking
| Setting | What It Controls | What It Doesn’t |
|---|---|---|
| Web & App Activity | Google searches, app usage, Assistant interactions | ISP tracking, OS-level activity |
| Chrome Browser History | Local browsing history | App usage, voice activity |
| Location History | Physical location data | Search or app behavior |
| Ad Settings | Ad personalization | Activity collection itself |
In short, Web & App Activity controls how Google personalizes your experience—not whether all tracking exists.
Should You Turn Off Web and App Activity?
There is no universal answer. It depends on how you use Google.
Keep It On If You
-
Use Google Assistant regularly
-
Rely on Google Maps for navigation
-
Want faster, context-aware search
-
Use multiple Google devices
Turn It Off If You
-
Strongly prioritize privacy
-
Rarely use Google services
-
Prefer privacy-focused tools
-
Don’t want long-term activity retention
Also Check: How to Open CROSH on a Chromebook (2025 Guide) — Fix Shortcut Issues & Run Commands
Best Option for Most Users (2025)
For most people, the smartest setup is to keep Web and App Activity on, enable automatic deletion, and manually remove sensitive searches when needed.
Turning Web & App Activity off does not make Google “stop tracking you entirely”—it only limits how activity is saved to your account and used for personalization.
How to Delete Web and App Activity
Turning the setting off does not delete existing data. Deletion is a separate action.

Manual Deletion
You can delete:
-
Individual activity items
-
A single day
-
A custom date range
-
All activity at once
Automatic Deletion
Google supports auto-delete every:
-
3 months
-
18 months
-
36 months
For most users, 18 months offers the best balance between privacy and usability.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
-
Assuming Chrome history and Web & App Activity are the same
-
Turning the setting off without deleting old data
-
Breaking Google Assistant unintentionally
-
Forgetting that voice and audio activity is included
-
Expecting ads to disappear completely
FAQs
Q. What is Web and App Activity?
Web and App Activity is a Google account setting that saves your searches, app usage, browsing activity, and voice interactions to personalize Google services like Search, Maps, and Assistant.
Q. Should I turn off Web & App Activity?
Only if privacy matters more to you than personalization. Most users benefit from keeping it on and enabling automatic deletion to limit data retention.
Q. How do I see all app and website activity?
Sign in to Google My Activity to view your searches, app usage, and website activity across Google services. You can filter results by date or product.
Q. What happens if I turn off Web and App Activity?
Google stops saving new activity, but past data remains unless you delete it. Search results become less personalized, and some features work less accurately.
Q. Is Web and App Activity the same as search history?
No. Search history is just one part of Web and App Activity, which also includes app usage, Assistant interactions, and Google service activity.
Conclusion
Web and App Activity isn’t a hidden trap—it’s a control system.
In 2025, the smartest approach isn’t disabling it blindly. It’s understanding what it collects, how it affects your experience, and how long that data is kept. With the right configuration, you can limit retention without losing the Google features you actually rely on.
Control the setting—don’t ignore it.
Related: Learn-Duck.web.app (2025 Guide): What It Is & How to Use It Safely
| Disclaimer: This content is provided for informational purposes only. Google’s features, settings, and data practices may change over time. Readers should refer to Google’s official documentation and their own account settings for the most current and accurate information. The author is not affiliated with or endorsed by Google. |